The enforced change to working from home (WFH) has had a massive impact on businesses, not just in the way they manage their employees and IT systems. As the COVID-19 pandemic progresses, enterprise IT teams are looking to answer key questions such as:
■ How has work from home affected the average working day?
■ Which applications have become more critical for working from home?
■ Has the rapid increase in collaboration app usage created a change in market leaders?
■ After the lockdown, will this become the new normal?
We set out to explore the answers to these questions and more in the second volume of our Global Remote Work Productivity Tracker series. The insights in this report are based on data aggregated from millions of employee devices at over 500 Global 2000 companies being managed via the Aternity digital experience management SaaS solution. We were able to pull anonymized information from all apps connected to our clients' environments.
Shifts in the Traditional Workday
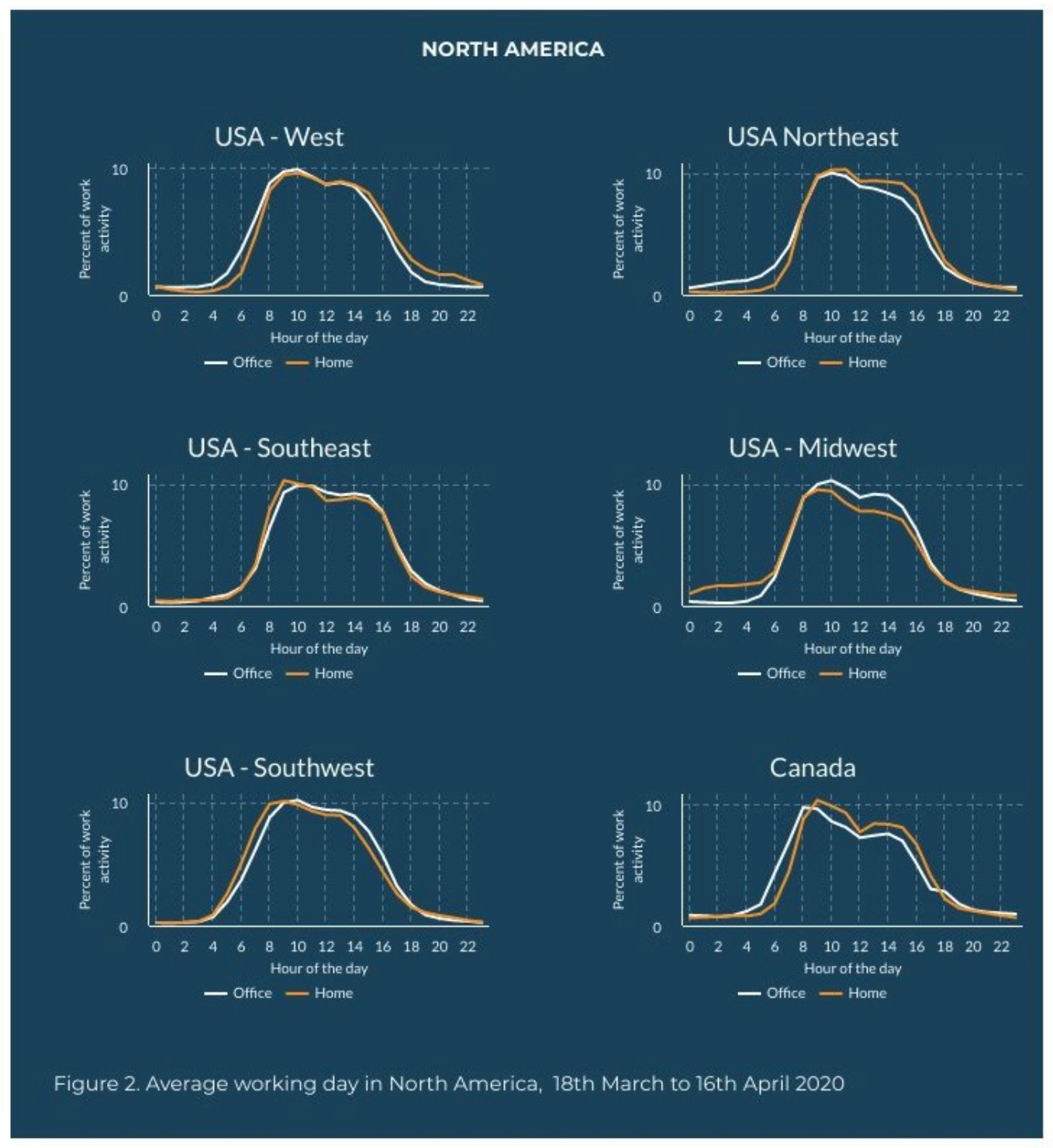
Now that the initial shock has worn off, the data shows that employees working from home are more productive with many workers embracing the lack of wasted time spent commuting and more flexible working hours to better manage their work-life balance.
In the United States, the knowledge worker-intensive regions of the Northeast and West are showing that workers are starting their days 30-60 minutes later in the morning and finishing later in the evening, possibly because of the lack of commuting.
However, the data shows an opposite shift is taking place in the Midwest with employees beginning their days earlier than in pre-COVID times. The difference is reflective of the fact that administrative staff who support round-the-clock manufacturing operations are now doing so from home. The lower level of remote work from late-morning to mid-afternoon likely reflects the need to tend to personal tasks, such as helping kids with home-schooling.
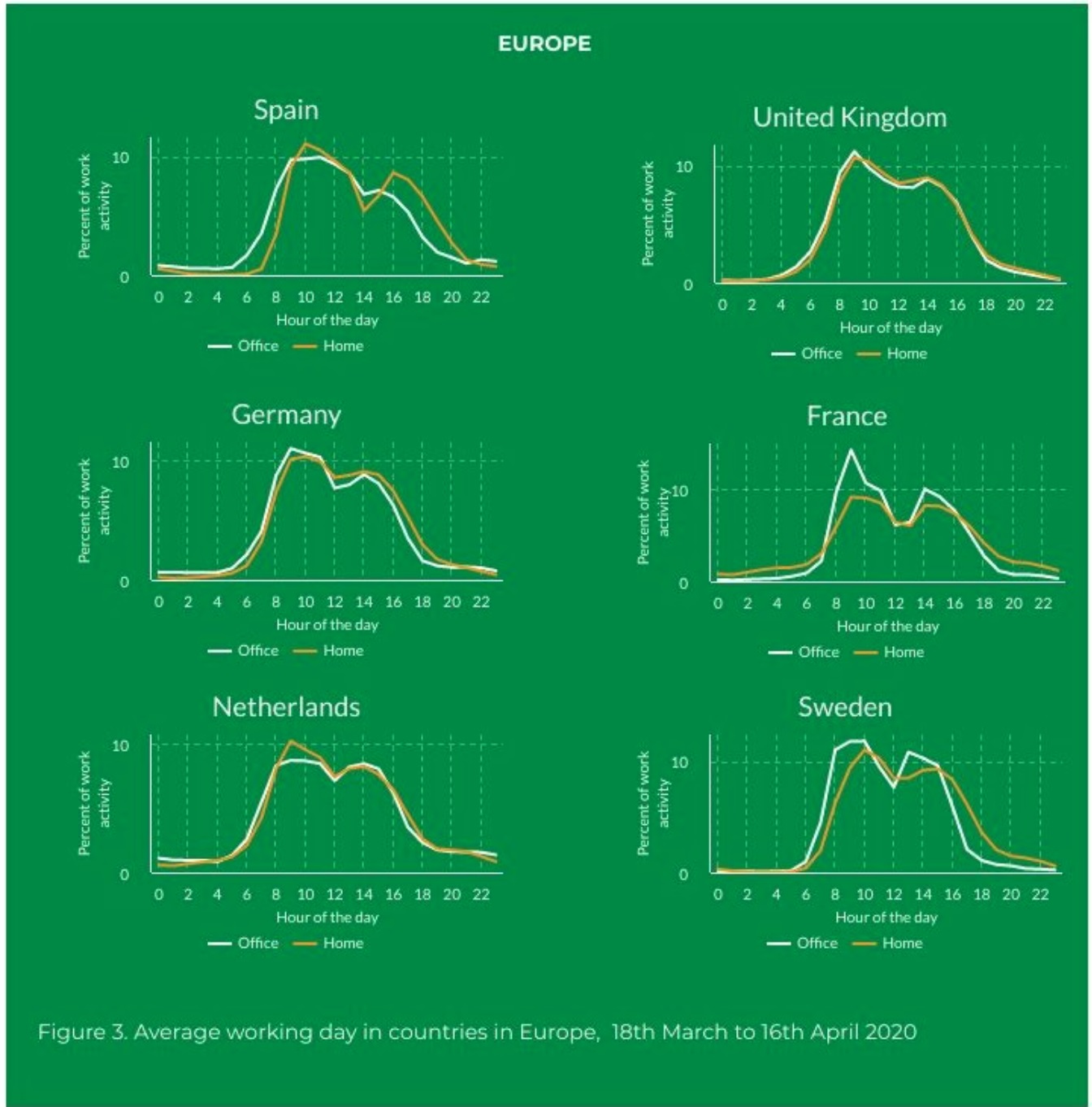
Europe reveals more differences by country than we see in the U.S., which is likely reflective of regional work cultures and differing impacts of the outbreak. In Spain and Sweden, remote workers started their day one to two hours later in the morning and ended later in the evening. Remote workers in France spread their activity more evenly throughout rather than front-loading it as they typically do.
Skype for Business Emerges as Early Winner in COVID-19 WFH Strategies
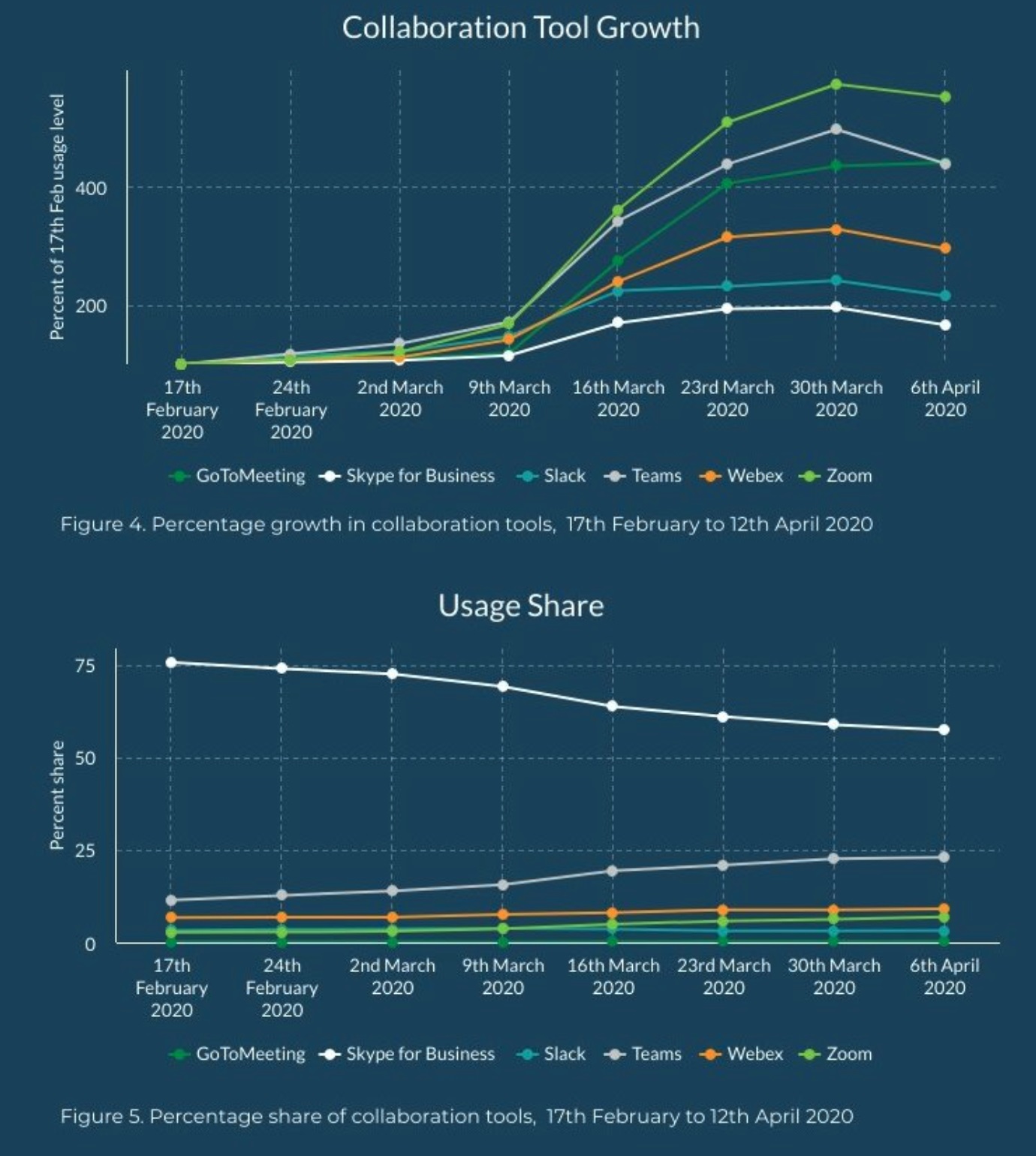
We are also seeing WFH changing the demands on different applications with, predictably, a significant increase in collaboration tools. We tracked the growth in usage of major collaboration tools from their "base" during the week of February 17, before the shift to remote work.
The increased use of synchronous collaboration and web conferencing tools was seen in all applications within the category. The highest growth was in Zoom, which peaked at 574% of its base usage during the week of March 30, followed by Teams, which peaked at 497% of its base usage during the same week.
The surprise winner from the COVID-19 WFH quarantine was Skype for Business. The app commands the highest share of usage by a wide margin, despite its usage declining incrementally before the pandemic. Microsoft Teams' share of usage has grown steadily during the same timeframe. As the pandemic timeframe extends, we expect Teams to continue to build its usage share as businesses that consider themselves "Microsoft Shops" push workers towards its rich collaboration capabilities over other similar applications they used when the initial transition to remote work occurred.
Microsoft Office's WFH Dominance
Microsoft hasn't made it a secret that usage of their enterprise productivity platform and associated apps have increased exponentially. Our data backs those claims up as Microsoft Office accounts for 38% of the total usage time and the highest share of usage coming from Outlook. With email replacing face-to-face communications and in some cases meetings as the result of the global shift to remote work, use of Outlook skyrocketed while other Office applications either remained the same or made incremental gains.
We've also seen non-work related web browsing from work computers increase 150% compared to late February. Web browsing overtook use of Outlook during the week of March 2 when panic over the outbreak peaked, suggesting workers spent considerable time reading the news to understand its impact during work hours.
After this initial massive surge in web browsing, it has generally plateaued or even reduced slightly as workers have adapted to their local shelter-in-place directives.
We expect to see employees and businesses continue to make adjustments to manage their "new normal." In the early going, we are seeing businesses rely heavily on trusted enterprise software brands like Microsoft to ensure their workers are productive during these historic times and expect this trend to continue. In the future, we'll be looking into app performance, device usage, and other trends affecting businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic so stay tuned.