The shift to hybrid and work-from-anywhere (WFA) models has become the norm, yet many organizations are struggling to provide their employees with a seamless digital experience. IT leaders often respond to performance complaints by upgrading computers and requesting users increase bandwidth, assuming that more bandwidth equals better performance. However, network (and therefore application) performance isn't just about connection speed — it's about reliability.
One of the most misunderstood culprits of poor application performance is packet loss. Even minimal packet loss can cripple the throughput of a high-speed connection, making enterprise applications sluggish and frustrating for remote employees. According to research conducted by Cloudbrink Inc., the 2025 Trends in Hybrid Work Report, 82.5% of IT professionals underestimate the impact of packet loss, leading them to invest in ineffective solutions.
So, what's going wrong? And why does adding more bandwidth fail to fix the issue?
The Hidden Cost of Packet Loss
For remote workers, network reliability depends on more than just available bandwidth. Many home supposedly "high speed" networks are plagued by unstable Wi-Fi connections, ISP congestion, and latency-inducing security tools. While a high-speed fiber connection might provide a gigabit of bandwidth, even a 0.005% packet loss rate can slash effective throughput by over 90%, according to research from the U.S. Department of Energy's Energy Sciences Network (ESnet). The research showed that the theoretical impact of packet loss matched almost exactly the actual impact. Sites such as https://packetloss.cloud/throuput-calculation/ provide a calculator so users can calculate the impact of packet loss under varying conditions.
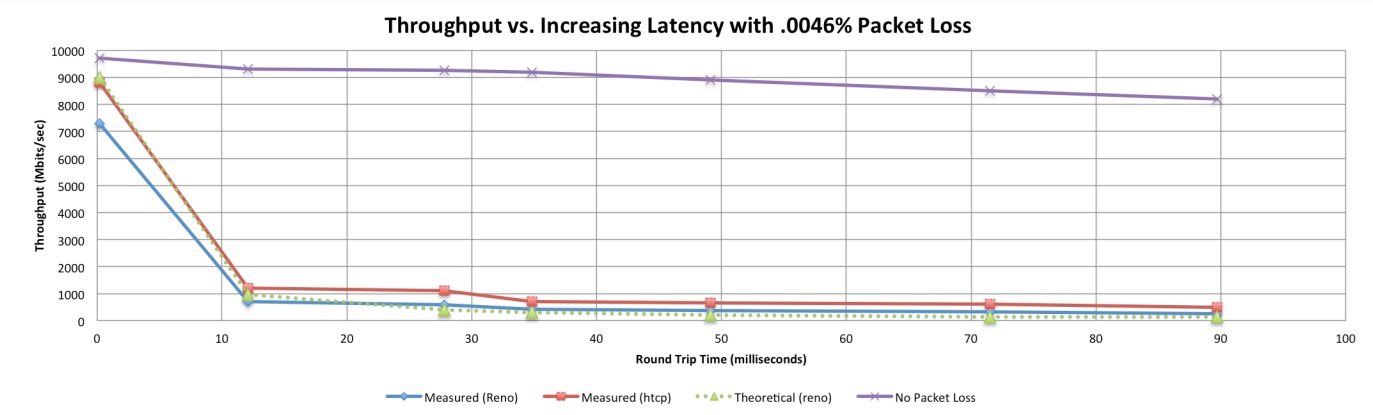
The reason the impact is so extreme lies in how TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) handles packet loss. When a packet is lost, TCP assumes congestion and slows down transmission to avoid exacerbation of the congestion. If packet loss is persistent — especially in networks with high latency — the connection's effective throughput can plummet, rendering collaboration tools, video conferencing, and cloud applications nearly unusable.
The Packet Loss Epidemic in Work-From-Anywhere Networks
The 2025 Trends in Hybrid Work Report revealed alarming statistics about packet loss across global regions:
- 60% of remote workers experience packet loss above 0.5%, which is enough to significantly degrade performance.
- North America sees an average packet loss rate of 1.8%, far exceeding the acceptable threshold for stable connections.
- IT teams are unaware of the real impact — only 17.5% believe that 0.5% packet loss has an extreme impact on user experience, despite overwhelming evidence to the contrary.
One of the key reasons packet loss is so damaging is that it disproportionately affects real-time applications like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Citrix virtual desktops. These tools rely on continuous data streams, meaning even small disruptions can cause jitter, freezes, or outright disconnections.
Why More Bandwidth Doesn't Fix the Problem
Many organizations attempt to combat poor performance by upgrading users to higher-speed internet plans, but this doesn't address the root cause. Here's why:
1. Packet Loss Is Not About Speed, It's About Stability: if a network drops packets due to congestion, interference, or poor routing, adding more bandwidth won't change how those packets are handled. When packets are dropped, the backoff is the same regardless of bandwidth.
2. Latency Compounds the Impact of Packet Loss: Secure access solutions like SASE and VPNs often add 70-110 milliseconds of latency. When combined with even minimal packet loss, a 1000 Mbps connection can behave like a 5 Mbps connection.
3. Home Wi-Fi and ISP Networks Are the Weakest Link: Most enterprise IT teams have no control over employees' last-mile connections, where Wi-Fi interference, ISP congestion, and network oversubscription create persistent packet loss.
Rethinking Performance for the Work-From-Anywhere Era
Instead of blindly increasing bandwidth, IT leaders need to focus on reducing packet loss where possible, reducing packet loss and latency impact, improving network resilience, and minimizing latency. Some key strategies include:
1. Mitigating Packet Loss with Advanced Error Recovery:
- Technologies that employ preemptive and accelerated packet recovery use techniques such as Forward Error Correction (FEC) or packet loss recovery algorithms that can help reconstruct lost packets before they impact application performance.
2. Reducing Latency in Secure Access Architectures:
- Latency exacerbates the impact of packet loss so solutions that minimize the latency penalty of VPNs and traditional SASE architectures can ensure security doesn't come at the cost of productivity.
- Solutions that break up the end-to-end connections into multiple shorter connections and deal with packet loss on a hop-by-hop basis can further reduce the end-to-end impact of packet loss.
3. Enhancing Visibility and Troubleshooting:
- IT teams need better tools to diagnose packet loss issues proactively, rather than reacting after remote employees report slow performance.
- For the work-from-anywhere generation, the whole end-to-end connection condition needs to be monitored, not just the mid-mile or first-mile. Data shows most of the issues are from the last mile and the access network where the user is connecting from.
Conclusion
The work-from-anywhere model is here to stay, but traditional approaches to network performance optimization are failing. More bandwidth doesn't equal better throughput when packet loss is present. Organizations must recognize that network reliability, not raw speed, is the key to ensuring a productive remote workforce.
By shifting focus from bandwidth upgrades to packet loss mitigation, latency reduction, and intelligent network optimization, IT teams can provide a seamless experience for their employees — wherever they work.
Final note
Interestingly, the survey from Cloudbrink showed that satisfaction levels among standard SASE users were the lowest. Participants ranked SASE lower on "ease of rollout," "end-to-end performance," and "support needs" compared to other technologies.
To read the whole of the study, visit cloudbrink.com/2025trends.
