
In the news last year, a core network change at a large service provider resulted in a major outage that not only impacted end consumers and businesses, but also critical services like 911 and Interac. At home, phone and internet service were down for the workday as millions were without service.
Modern distributed and ephemeral systems have connected us better than ever before, and the latest ChatGPT phenomenon has opened the possibility for new and mind-blowing innovations. However, at the same time, our dependency on this connected world, along with its nonstop innovations, challenges our ethos with important questions and concerns around privacy, ethics, and security, and challenges our IT teams with outages of often unknown origin.
When it comes to system outages, AIOps solutions with the right foundation can help reduce the blame game so the right teams can spend valuable time restoring the impacted services rather than improving their MTTI score (mean time to innocence). In fact, much of today's innovation around ChatGPT-style algorithms can be used to significantly improve the triage process and user experience.
In the monitoring space, impact analysis for services spanning application to network or cloud to mainframe has known gaps that, if solved, can have a big impact on service availability. Today, these gaps require human intervention and result in never-ending bridge calls and the blame game where each siloed team responsible for applications, infrastructure, network, and mainframe are in a race to improve their MTTI score. This, unfortunately, also has a direct impact on customer experience and brand quality.
The challenge faced by teams is a layering issue, or "Layeritis." For each layer, different kinds of monitoring solutions are used. Each solution, in turn, has its own team and applies different techniques like code injection, polling, or network taps. This wide spectrum of monitoring techniques eventually generates key artifacts like metrics, alarms, events, and topology that are unique and useful in the given solution but operate in silos and do not provide an end-to-end impact flow.
Tool spam leads to a noise reduction challenge, which many AIOps tools solve today with algorithmic event noise reduction using proven clustering algorithms. However, in practice, this has not been proven to get to root cause. The hard problem is root cause isolation across the layers, which requires a connected topology (knowledge graph) that spans the multiple layers and can deterministically reconcile devices/configuration items (CIs) across the different layers.
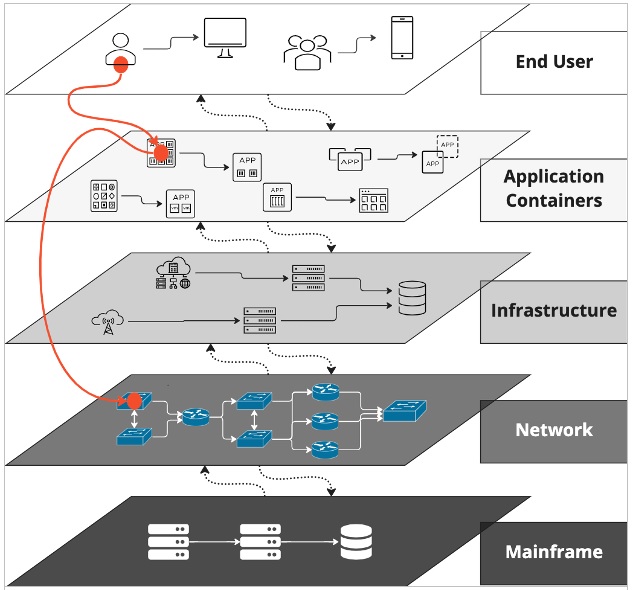
Challenge of root cause isolation across the siloed application, infrastructure, network, and mainframe layers.
Seven Steps to Cure Layeritis
The solution to an AIOps Layeritis challenge requires planning and multiple iterations to get right. Once steps 1-3 are in a good state, steps 4-7 are left to AI/machine learning (ML) algorithms to decipher the signal from the noise and provide actionable insights. The seven steps are as follows:
1. Data ingestion from monitoring tools representing the different layers to a common data lake that includes metrics, events, topology, and logs
2. Automatic reconciliation across the different layers to establish end-to-end connectivity.
■ Since end user experience is tied to service health score, include key browser performance or voice quality metrics.
■ Application topology to underlying virtual and physical infrastructure for cloud, containers, and private data centers (e.g., APM tools may connect to the virtual host, but will not provide visibility to the underlying physical infrastructure used to run the virtual hosts).
■ Infrastructure connectivity to the underlying virtual and physical network devices like switches, routers, firewalls, and load balancers.
■ Virtual and physical infrastructure connectivity to the mainframe services like DB2, MQ, IMS, and CICS.
3. Dynamic service modeling to draw boundaries and build business services based on reconciled layers.
4. Clustering algorithm for noise reduction of events from metrics, logs, and alarms within a service boundary.
5. Page ranking and network centricity algorithms for root cause isolation using the connected topology and historical knowledge graph.
6. Large Language Model (LLM)/Generative AI (GPT) algorithm to build human-readable problem summaries. This helps less technical help desk resources quickly understand the issue.
7. Knowledge graph updated with the causal series of events (aka a fingerprint). Fingerprints are compared with historical occurrences to help make informed decisions on root cause, determine the next best action, or take proactive action on issues that could become major incidents.
For algorithms to give positive results with a high level of confidence, good data ingestion is required. Garbage data will always give bad results. For data, organizations rely on proven monitoring tools for the different layers to provide artifacts like topology, metrics, events, and logs. Additionally, with metrics and logs, it's possible to create meaningful events based on anomaly detection and advanced log processing.
Below are three use cases that focus on common issues today's IT teams face, which can be resolved using AIOps in a single consolidated view to identify the root cause and automate the next steps:
Use Case 1: Application issue where infrastructure and network are not impacted. Here, AIOps will only identify the impacted application software components.
Use Case 2: Network issue where infrastructure and application are impacted, but not at fault.
Use Case 3: Mainframe database issue where connected application running on distributed infrastructure is impacted.
In each use case above, AIOps removes the need for time-intensive investigation and guesswork so your team can see and respond to issues — even before they affect the business — and focus on higher-value projects.
Overall, AIOps solutions can provide visibility and generate proactive insights across the entire application structure, from end user to cloud to data center to mainframe.
