Public Cloud provides a layer of abstraction between the functionality of a service and its delivery. Put simply, its functionality is unlocked by a credit card versus actual hands-on deployment. This is both a blessing and a curse.
Public Cloud customers are finding that, while Cloud services are easy to consume, they are not as easy to govern and manage. This abstraction layer means that traditional Application Performance Management (APM) solutions may not be as useful as they once were. As a result, many CIOs are finding it necessary to reevaluate management portfolios for Cloud-readiness.
Throughout most of 2011 and into 2012, Enterprise Management Associates’ (EMA) Application Management team conducted back to back research projects on APM for Cloud services. The research began during the Spring of 2011 with survey-based research assessing the impact of Cloud in all its flavors—public, private, and hybrid—on IT organizations.
After publishing the results of this study in August, we utilized the findings to formulate an EMA Radar Report, essentially an assessment of the solutions of eighteen leading APM vendors for “Cloud-readiness”. Released earlier this month (February, 2012), the findings are available for download at. www.emausa.com
The August report revealed that today’s companies are much further along in their Cloud deployments than most experts would have suspected. Nearly 85% are either already using private Cloud or are planning to do so within the next year. For SaaS that number is approximately 75%, for IaaS it is 65%, and for IaaS it stands at approximately 55%.
While these numbers are definitely interesting, to understand the true impact of Cloud it is necessary to take a look at how companies are using these services. After all, regardless of the underlying delivery mechanism, applications are still IT's primary deliverable, and application performance is the key measure of application quality. For this reason, the study also asked detailed questions about enterprise applications, architectures, and the role of Cloud in supporting production applications.
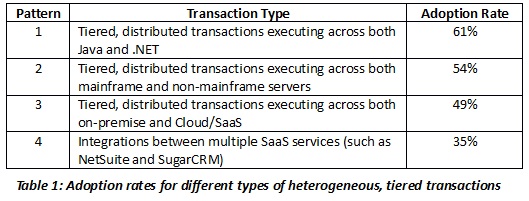
Table 1 shows adoption rates for a variety of deployment patterns for integrated applications. It illustrates the fact that transactions spanning heterogeneous hardware and software platforms are commonplace, definitely mainstream, and that those spanning on-premise and Cloud are not far behind.
Cloud-Ready APM
Patterns 1 and 2 relate to on-premise-hosted transactions. Patterns 3 and 4 relate to transactions touching the public Cloud, and, in the case of Pattern 4, integrations between multiple SaaS platforms.
While most of the APM solutions in the marketplace today were originally engineered to support primarily on-premise applications, many still do not support Patterns 1 and 2. They lack support for transactions spanning on-premise and mainframe or for those spanning Java and .NET.
APM solutions also vary widely in their levels of support for troubleshooting and root cause analysis. If the requirement is to quantify performance and availability, an application performance monitoring solution may suffice. However if there is an additional requirement for in-depth troubleshooting/root cause analysis support, monitoring solutions alone cannot provide adequate depth of visibility.
EMA’s APM taxonomy distinguishes performance monitoring from performance management for just this reason. In doing so, it makes the following distinctions:
Application Management Solutions: These solutions deliver visibility to and control of transactions, applications, and end-to-end services. The terminology covers a broad range of capabilities and products with visibility to application execution from a wide variety of instrumentation points.
Application Performance Monitoring and Application Performance Management are subsets of Application Management that focus on performance. The two classifications differ in their levels of support for troubleshooting and root cause analysis.
- Application Performance Monitoring solutions, such as End User Experience (EUE) management products, assess performance and availability.
- Application Performance Management (APM) solutions also monitor performance but support troubleshooting, problem determination, and root cause analysis as well. In other words, they have some level of visibility to the service model, which is the relationship between “top down” execution and “bottom up” infrastructure.
It is important to understand these distinctions because, although a wide variety of products are being marketed under the “APM” category, they are quite variable in terms of their capabilities. Monitoring solutions tend to be relatively inexpensive and may well be good choices if the requirement is simply to quantify performance and availability. Management capabilities do add cost, but that cost can quickly be recouped when automated troubleshooting replaces “all hands on deck” root cause analysis marathons.
Patterns 3 and 4 are examples of additional reasons why these distinctions are important. The adoption percentages for Pattern 3, for example, demonstrate that on-premise/public Cloud integrations are definitely mainstream deployment patterns. However, APM solutions vary significantly in the way they handle such transactions once they exit the enterprise IT ecosystem.
While virtually all have some depth of visibility to the on-premise segment of end-to-end execution, many see the public Cloud as a “black box”. They can monitor transactions to and from, and in doing so extrapolate “Cloud” performance. However they cannot penetrate beyond (or within) such integrations to a level that supports full-spectrum, tier-based reporting. Such reporting is essential for actually managing and troubleshooting complex applications.
This problem is even more prevalent in Pattern 4 deployments, since the majority of APM solutions have no visibility to the integration technology supporting SaaS to SaaS integrations. This is another case where off-premise tiers appear as a single black box as opposed to a series of steps with quantifications of execution time at each step.
Summary
What does this all this mean to CIO’s? One global bank is monitoring performance of customer applications from multiple locations worldwide. When they receive performance alerts, they manually triage to determine whether the problem is from all locations or a single location. They then do further manual triage to determine the actual problem source. Sound familiar? It should, because this is the same, quintessential problem-solving paradigm IT has utilized for eons—only now it is on a broader scale.
Cloud, particularly public Cloud, means that the underlying structure of transactions and applications becomes more opaque. Performance problems become more difficult to troubleshoot. Supporting these new distributed applications cost-effectively requires APM solutions that are up to the task. Now is a good time for CIOs and their teams to reevaluate and, if necessary, shore up their APM solutions to accommodate this new complexity. Otherwise, it is far too easy to end up with the “same old same old”— fifteen IT specialists missing their kid’s soccer games to figure out why business critical services aren’t performing to user expectations.


