Although CMDBs grew up with a focus more on process control than on performance management and real-time actions, design advances and new trends such as cloud computing are changing that dramatically. Operational professionals with concerns such as Mean-Time-to-Repair (MTTR) and Mean-Time-Between-Failure (MTBF) can benefit greatly from a “reconciled view of truth” including the impacts of change on performance, both of which are ultimately dependent on a CMDB/CMS foundation.
Some of the more dramatic use cases here include:
A Reconciled View of Truth Across Many Multiple Sources: One CMDB/CMS initiative reduced Mean-Time-to-Repair (MTTR) 70%, when downtime costs were estimated at $1 million a minute, by providing a more cohesive way of leveraging its many monitoring tools, and consolidating down to a single service desk.
Reflexive Insights into Change and Configuration for Diagnostics: Automating insights between configuration and change issues and performance issues to support real-time or proactive diagnostics is a core value of a service impact CMDB/CMS.
Validation that a Newly Provisioned Service is Performing Effectively (or not): Once a service has been deployed, what for instance is the impact on end-user experience?
Incident and Problem Management Automation and Governance: When CMDB/CMS is combined with strong support ITIL or other workflows and process definitions, it can accelerate the time to resolve problems and harden desired processes so that they are more consistently followed.
Finding the Owner: Automating and securing the process of finding individuals who “own” a problem or CI, though seemingly trivial, can nevertheless bring significant benefits –- up to $100,000 a year in just opex-related phone time between the service desk and operations in the case of one EMA client.
Business Process and Service-Specific Benefits: Having a cohesive vision of “truth” can positively impact business processes as far ranging as loan processing, to hospital management and admissions, to manufacturing line efficiencies, as just a few examples.
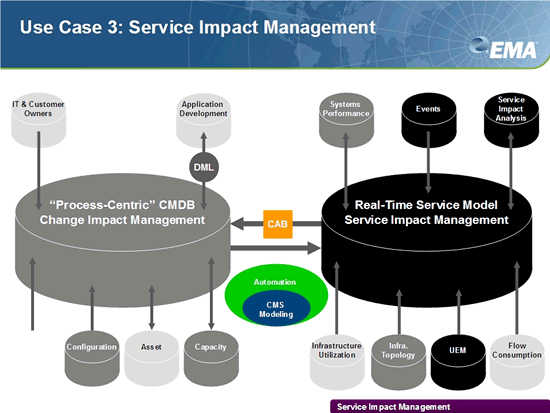
Figure 1: Service Impact Management prioritizes more real-time, operational insights and is in many respects a complementary technology to more process-centric, traditional CMDBs. However, both are anchored core insights into application-to-infrastructure and infrastructure-to-infrastructure interdependencies.
From a Service Impact perspective, EMA identified the following four Value Leaders:
AccelOps
AccelOps was third from the highest score in overall rankings and first in Deployment and Cost Efficiency as well as Functionality. AccelOps is often purchased as a service management system with strong capabilities in discovery, security, application dependency and CMDB modeling. Its deployments are consistently efficient and quickly lead to value, and so AccelOps is well optimized to the requirements of virtualized, cloud and hybrid environments.
ASG
ASG came in first in its overall vendor score. ASG has unique capabilities for assimilating third-party information, including that from performance management solutions to complement or supplement its own. It also has a healthy ability to federate and adapt to real-time insights. Combine this with strong application discovery and dependency mapping, solid dashboards, and a suite of its own monitoring tools –- and its position in the sun here is clear. As you may remember, ASG was also a value leader in Asset Management and Financial Optimization.
FireScope
FireScope was at the top for Deployment and Cost Efficiency for Service Impact Management, within the top three for Architecture and Integration and within the top third for Functionality. In addition to FireScope’s strong capabilities for Service Impact Management via its own product -- Unify, Orchestrate also profited from attractive dashboards -- including mashups, and a flexible way of assimilating third-party solutions that includes putting a “freshness stamp” on incoming data. FireScope won an award for “Most easily administered CMDB.”
Interlink
Interlink excelled in all functional and deployment areas. Interlink’s Service Configuration Manager is optimized to work with its Business Enterprise Server (BES) where it provides a complete system for Service Impact Management. It leverages insights into the impact of change, and has a far-reaching capability to assimilate interdependencies across the full service infrastructure from third-party sources. Interlink is a small vendor based in Edinburgh, Scotland, but it does have customers in the U.S. Its customers give it very high praise for its support.
Click here to read the CMDB/CMS use cases for Change Management and Change Impact Analysis
Click here to read the CMDB/CMS use cases for Asset Management and Financial Optimization
